What to Do About Anxiety & Insomnia! How to Relax and Sleep Well Every Night?
Insomnia is believed to be a prevalent urban ailment among the majority of Hong Kongers. Statistics show that out of every 10 Hong Kong residents, up to 7 suffer from insomnia. The primary causes include rapid lifestyle pace, overwhelming work pressures, and excessive busyness, leading to a decline in quality of life and continuous disruption of everyday routines and habits.

Without good nights, how can you have good days?
Sleep quality is a significant concern as it affects your energy levels the next day. Additionally, when you worry about being unable to sleep, you become more anxious and find it even harder to fall asleep. Poor sleep affects your work or academic performance and exacerbates feelings of tiredness and irritability.
Have you identified the reasons for your insomnia? Work, studies, emotions, stress, and illness can all contribute to sleepless nights. Moreover, using smartphones before bed, binge-watching, or planning activities for the next day may also disrupt your sleep.
Patients with mental health conditions such as depression, bipolar disorder, or schizophrenia may also experience sleep disturbances.
To effectively resolve anxiety-related insomnia, understanding the mechanisms of sleep is crucial.
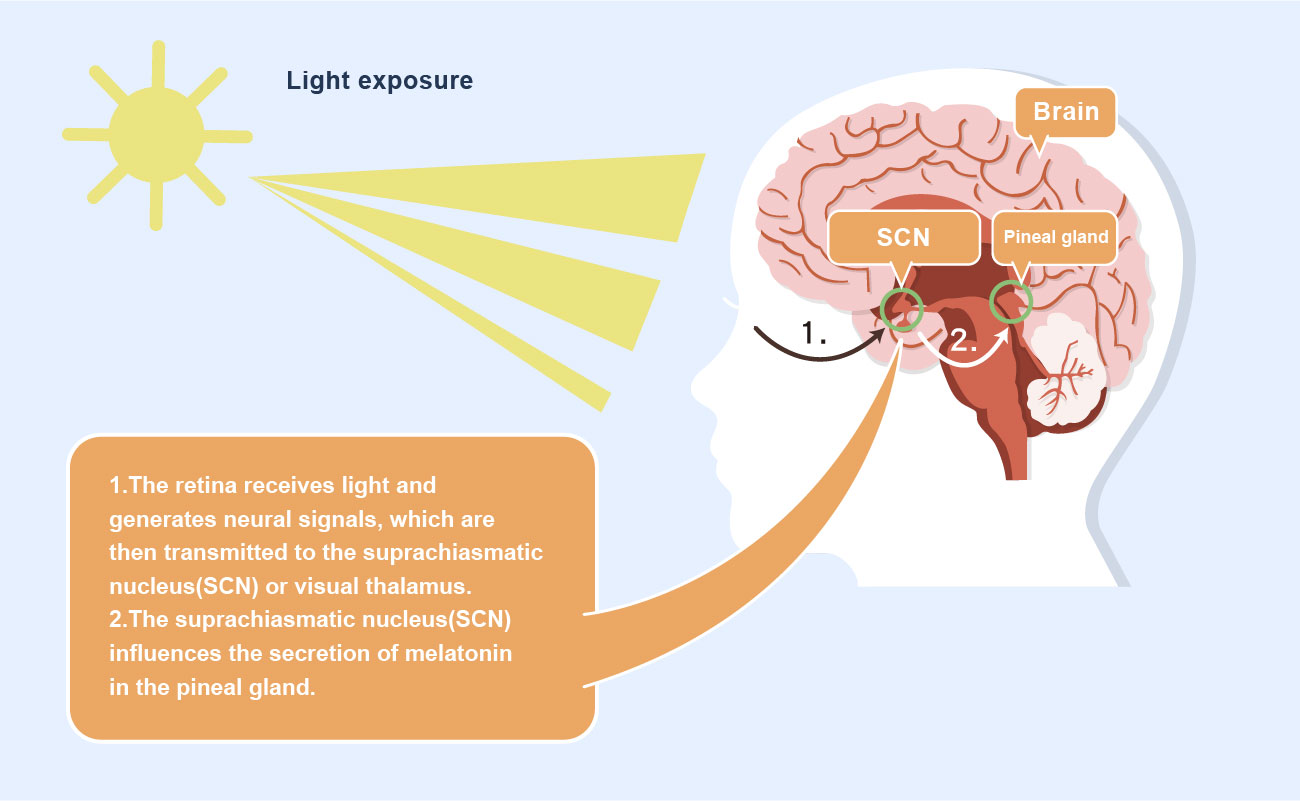
Why can we be active during the day and sleep at night?
The primary operation of the human circadian rhythm depends on regulation of the suprachiasmatic nucleus and the secretion of melatonin by the pineal gland.
- The regulation of suprachiasmatic nucleus(SCN) in the central nervous system:
When the retina receives light, it sends signals to the suprachiasmatic nucleus in the brain, which in turn affects the secretion of melatonin in the pineal gland. Melatonin secretion is inversely proportional to the intensity of light. Therefore, melatonin secretion is inhibited in environments with sunlight or artificial light. However, in the evening, the pineal gland increases melatonin secretion. - Melatonin secretion serves the following functions:
– Induces sleepiness and initiates sleep.
– Regulates sleep duration to maintain adequate sleep hours.
The Sleeping cycle can be divided into:
- Non-rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep: During this stage, the eyes do not move, and the body’s blood pressure, heart rate, and temperature decrease.
- Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep: Characterized by eye movement, relaxation of muscles except for the diaphragm muscles: To ensure that the body and limbs do not move erratically during dreams, thereby preventing danger.
Anxiety-related insomnia is related to melatonin and serotonin.
Melatonin has two main effects on sleep:
- Induces sleepiness and initiates sleep.
- Regulates the transition from sleep to wakefulness to maintain adequate sleep hours.
The impact of melatonin on sleep is evident. For instance, children under five typically sleep between 10 and 15 hours, while adults sleep between 7 and 9 hours. However, as individuals age, melatonin secretion decreases, reducing sleep time to 5 to 8 hours.
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that must be obtained through diet because the human body cannot synthesize it. Tryptophan is crucial because it is the precursor to serotonin, which can be converted into melatonin. Both serotonin and melatonin are closely related to sleep.
Taking 1-1.5 grams of tryptophan before bedtime effectively shortens the time it takes to fall asleep. Studies have found that consuming foods rich in tryptophan (Tryptophan) a few hours before bedtime can help sleep.
One of the main factors affecting sleep is serotonin, as it helps calm and relax the body. Once serotonin levels are low, it can lead to irritability and poor sleep.
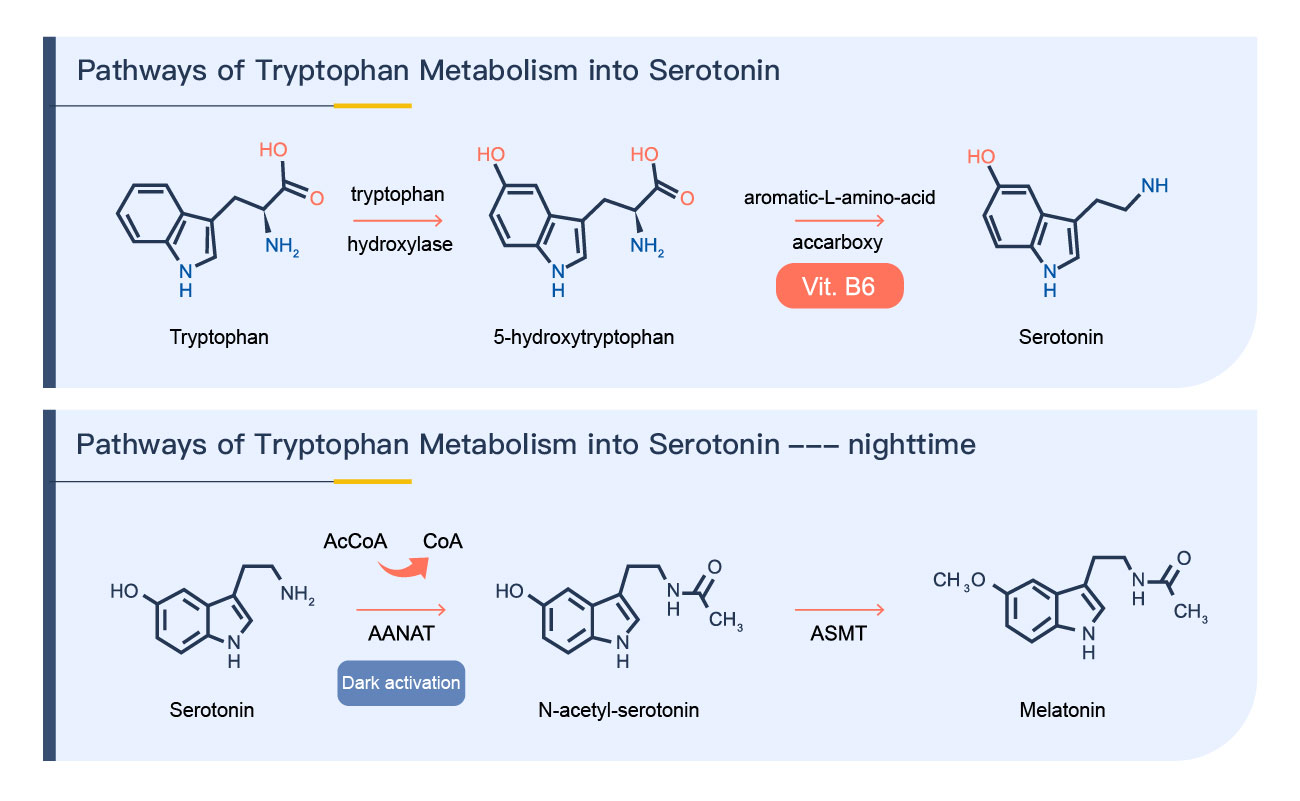
In addition to melatonin and serotonin, 5-HTP is essential for improving sleep. Its mechanism involves promoting serotonin synthesis in the brain to convert it into sufficient melatonin to aid sleep. However, not everyone benefits from supplementing with 5-HTP for sleep. For individuals with sufficient serotonin levels, supplementation with “5-HTP” may not be beneficial (due to limited conversion enzymes). Generally, supplementation with “5-HTP” has a noticeable improvement for insomnia caused by conditions such as depression or similar conditions (due to lower serotonin levels in the brain).
Over-reliance on sleeping pills may not solve anxiety-related insomnia.<
When unable to sleep, most people immediately think of sleeping pills. These medications often suppress the central nervous system, block pathways between nerves and the brain, and force the body to shut down. Since the effects of these medications are fast and the body metabolizes them quickly, there are fewer side effects, such as dizziness or drowsiness the next day.
However, due to their effectiveness, prolonged use can lead to dependency, resulting in people using them without a doctor’s prescription:they can increase the dosage on their own, and cause the brain’s receptors to become fatigued, leading to ineffectiveness. Additionally, sleeping pills only temporarily relieve insomnia and cannot eliminate its causes, such as hormonal imbalances caused by stress, anxiety, or situations where, despite being tired, people cannot fall asleep.

Somniphyt® Total Night is a natural herbal solution to relieve anxiety-related insomnia.
Many Hong Kong people consume sleep supplements to continuously and effectively improve insomnia, premature awakening, or frequent dreams. Somniphyt® Total Night is formulated with four natural herbal ingredients, amino acids, and melatonin to help alleviate anxiety-related insomnia, excessive work stress leading to nervous tension, and restlessness.
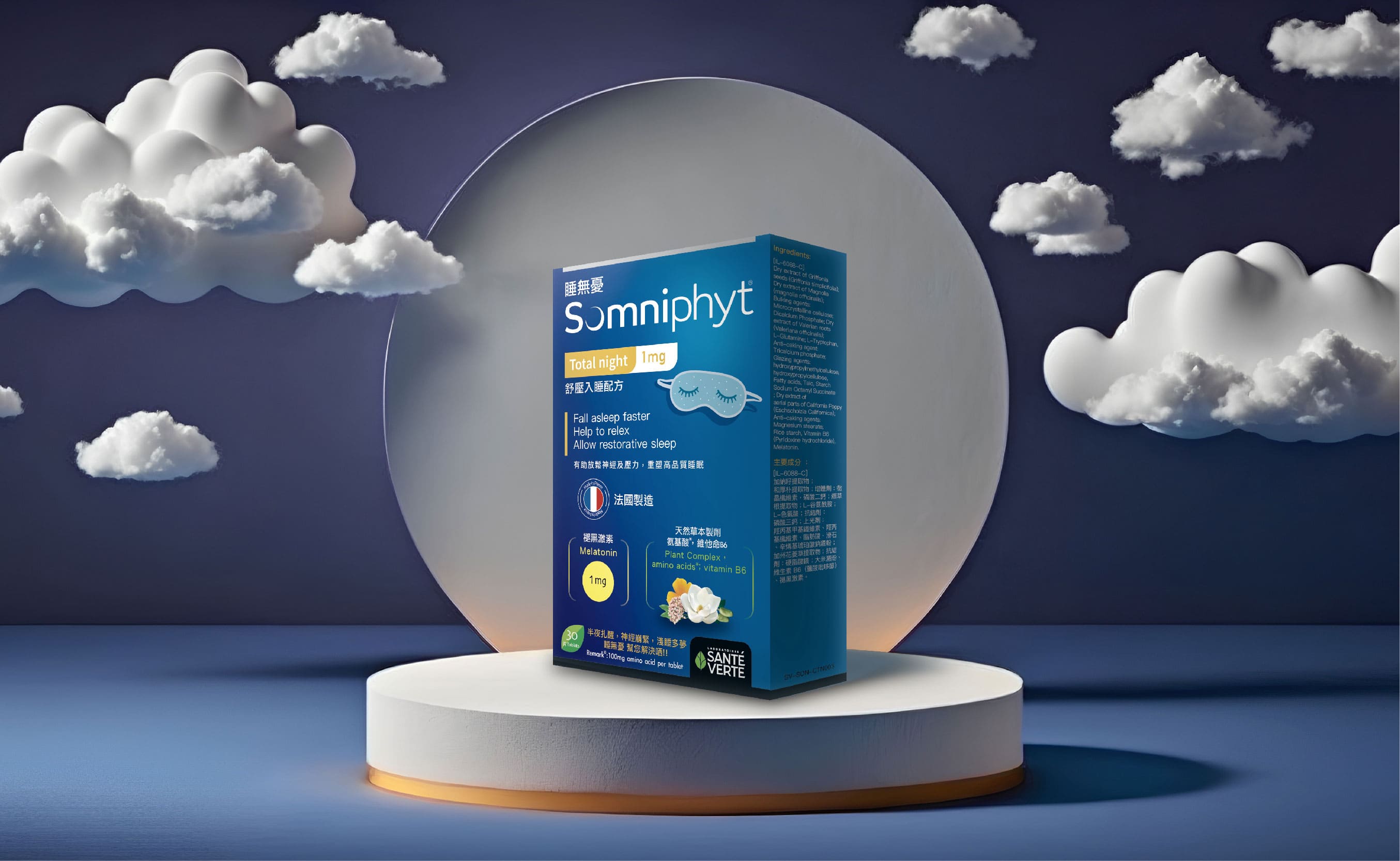

Ingredients of Somniphyt® Total Night Formula
Herbal Ingredients:
Griffonia Seed Extract
5-HTP (5-Hydroxytryptophan) is a pure natural herbal formula derived from Griffonia simplicifolia seeds, an extract from the seeds of a West African medicinal plant. It has a calming effect and serves as a precursor to 5-HT. Under the action of Decarboxylase, it generates 5-HT, which increases the activity of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the body and enhances serotonin production in brain cells, thereby increasing the content of 5-HT. It can improve sleep quality, help suppress appetite, reduce carbohydrate intake, and lower stress hormones. 5-HTP is a precursor to serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine), which can pass through the Blood-Brain Barrier directly to the brain to synthesize serotonin. During nighttime, serotonin converts into melatonin to aid sleep, making 5-HTP essential for addressing insomnia.
Magnolia Bark Extract
Research reports indicate that Honokiol (Magnolia Bark Extract) significantly increases Non-Rapid Eye Movement(NREM) sleep duration. Honokiol increases the transition frequency from wakefulness to NREM sleep and subsequently from NREM sleep to wakefulness. By regulating GABAA receptors, Magnolia Bark Extract promotes NREM sleep, indicating its potential application in sleep therapy.
Valerian Extract
Valerian induces sleep by interacting with central GABA receptors. It increases GABA concentrations by inhibiting the enzyme responsible for GABA metabolism, reducing central nervous system activity. Valerian also stimulates GABA release and reuptake and directly binds to GABA-A receptors. Valerian is considered one of the most promising sleep aids and is believed to promote melatonin release through 5-HT2A receptors.
Amino Acids:
L-Tryptophan
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that must be obtained through diet and is crucial for synthesizing serotonin, a precursor to melatonin. Both serotonin and melatonin are closely related to sleep.
L-Glutamine
Glutamine primarily acts as a precursor to help synthesize other amino acids and glucose for energy production and is a precursor to GABA synthesis. GABA is a naturally occurring amino acid in the human body, primarily found in the brain and eyes, composed of glutamine and glucose. GABA mediates physiological functions, aiding sleep and maintaining health. GABA is essential for inhibiting neural transmission in the body. Research has found that sleeping can produce enough GABA because GABA levels are high during deep sleep.
Vitamins:
Vitamin B6
B6 is associated with mood regulation and has the most significant relationship with the causes and treatment of anxiety. B6 affects the neurotransmitter serotonin, which controls depression and anxiety. The conversion of 5-HTP to serotonin requires the action of Decarboxylase, and vitamin B6 assists this enzyme’s function.
Melatonin
Melatonin is a hormone secreted by the pineal gland in the brain, playing a vital role in regulating the body’s circadian rhythm. Melatonin levels in the human body fluctuate periodically, peaking at night and decreasing during the day. The results of a comprehensive 2013 study also show that melatonin improves primary sleep disorders, such as:
- Shortening the time it takes to fall asleep
- Increasing overall sleep duration and improving sleep quality.
Many people believe that melatonin has fewer side effects and is not addictive. Current research indicates that taking 2 mg of sustained-release melatonin daily for six months has not resulted in severe side effects, nor has long-term continuous use led to tolerance (meaning that the effects gradually decrease after continuous supplementation).
If you decide to take melatonin, taking it 30 minutes before bedtime is generally recommended, starting with a low dose of 0.5 mg. If the effect is not ideal, consider increasing the dose to 3-5 mg.


