There are many ways to address insomnia, but the primary step is identifying the root cause.
The frustration of insomnia can lead to stress and loneliness, causing more harm than the insomnia itself. Insomnia can be categorized into several types, with waking up in the middle of the night and having difficulty falling back asleep being the most common. If this condition persists for a month and occurs at least three days a week, it significantly impacts quality of life. Fortunately, there are more solutions to insomnia than challenges. By identifying the source and remaining open-minded, trying different methods can undoubtedly solve the problem of insomnia.

Definition of Insomnia
The World Health Organization has a diagnostic standard for insomnia:
- Difficulty falling asleep and poor sleep quality.
- Sleep problems occur at least three times a week for at least one month.
- The impact of sleeping problems is thought about during the day and at night.
Four Different Types of Insomnia
- Difficulty falling asleep: Difficulty falling asleep after lying down, needing more than 30 minutes to fall asleep. Patients with anxiety disorders are most common.
- Inability to maintain deep sleep: Waking up intermittently and unable to enter the deep sleep stage.
- Inability to recover from fatigue after waking up: Feeling unable to recover from fatigue after waking up, as if you have not slept.
- Early awakening: Waking up in the middle of the night or early morning, tossing and turning, and having difficulty falling asleep. Patients with endogenous depression are the most common. The waking time is usually 1-2 hours earlier than usual, occurring at least three nights a week. During the day, you may feel drowsy, irritable, emotionally low, and anxious.
Primary Causes of Insomnia
Many factors contribute to insomnia, sometimes a combination of several factors. The most common reasons include:
- Psychological factors: Stress, anxiety, depression.
- Physiological factors: Cold, sleep apnea, bone pain, indigestion, high liver index, hyperthyroidism.
- Environmental factors: Room lighting, noise, temperature.
In addition to the above reasons, using smartphones before bed is the most mainstream cause of insomnia in modern urbanites.
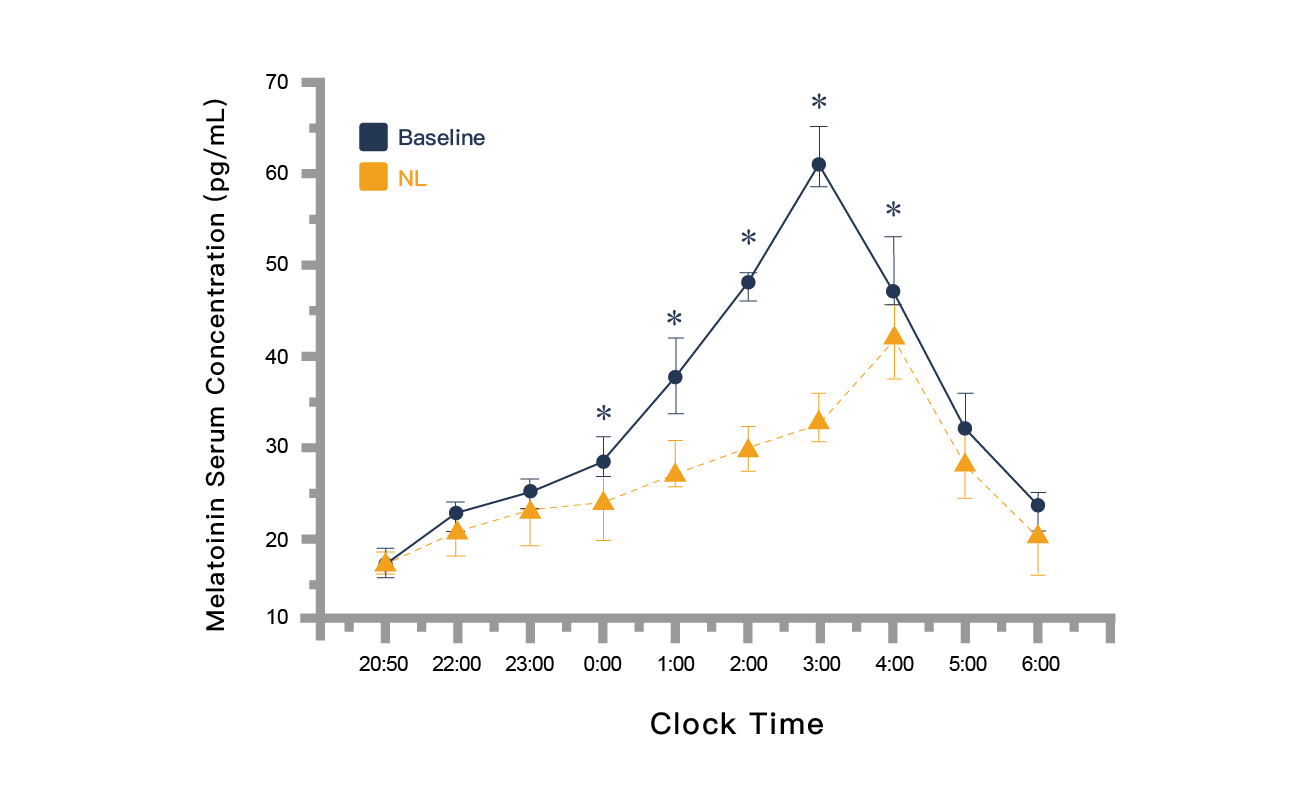
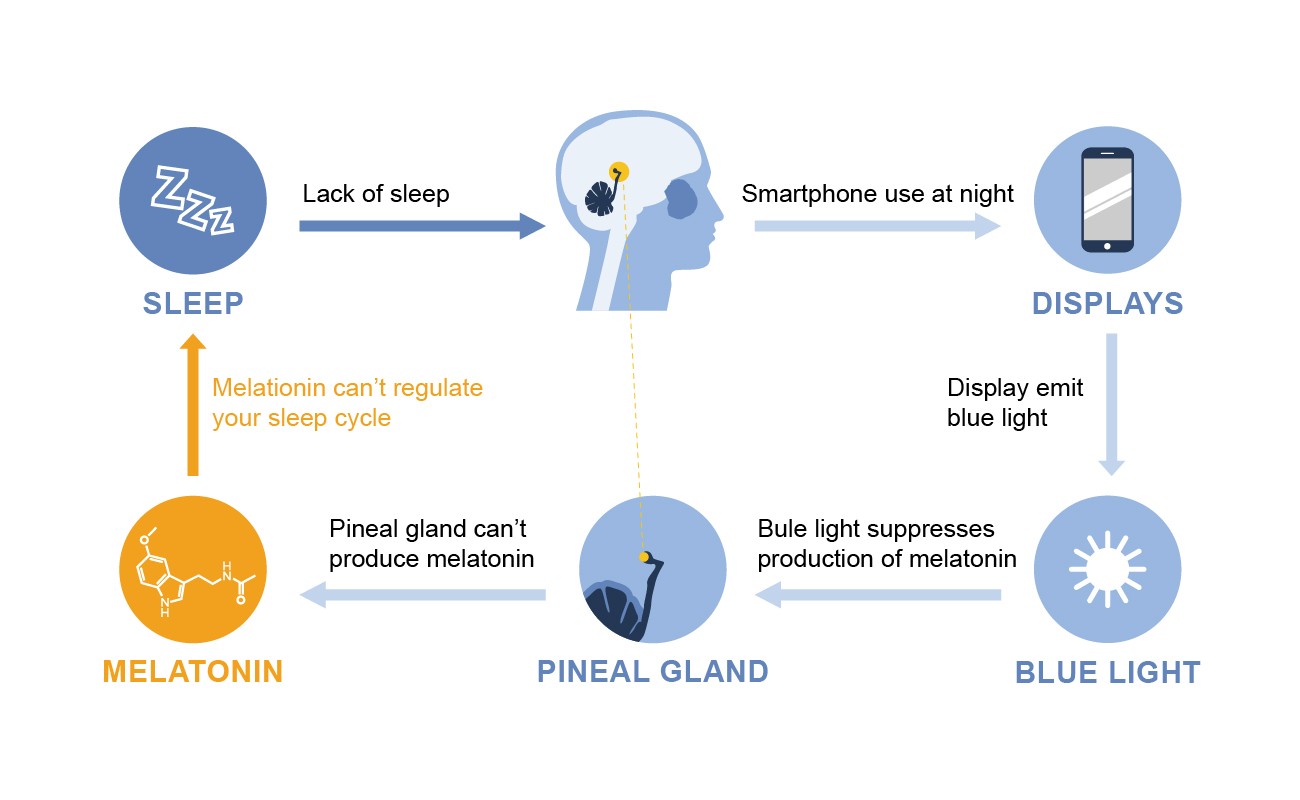
When the light weakens at night, the pineal gland in the brain secretes melatonin, promoting sleepiness. However, the screens of electronic devices contain much blue light. After the blue light enters the retina, it converts into nerve signals transmitted to the brain’s suprachiasmatic nucleus, then to the pineal gland. The pineal gland receives incorrect messages, perceiving it as daytime, inhibiting and delaying melatonin secretion and reducing drowsiness. Unable to fall asleep, people get up to use electronic devices, forming a vicious cycle.
Five Solutions for Insomnia
Occasional insomnia doesn’t affect health significantly, but chronic insomnia can lead to depression, anxiety, substance abuse, alcoholism, suicide, increased risk of hypertension and diabetes, and even shortened lifespan. It also affects work, study, and social activities.
- Start with sleep habits: Cultivate regular sleeping and waking times, avoiding oversleeping.
- Relaxation: Try meditation or other relaxing activities before bed, such as reading, listening to music, doing relaxation exercises, or taking a warm bath, to relax the mind.
- Exercise: Regular exercise during the day is an excellent way to relax the nerves, but avoid vigorous exercise before bed to avoid tension.
- Avoid overeating or hunger: Both hunger and overeating increase gastric burden, making it difficult to fall asleep. Avoid consuming caffeine-containing foods in the afternoon.
- Take supplements containing melatonin and herbal ingredients before bed.
Introducing Somniphyt® Total Night LP<
Somniphyt® Total Night LP is a unique supplement with four natural herbal ingredients, amino acids, and melatonin. It helps you address anxiety-induced insomnia, shallow sleep with many dreams, waking up in the middle of the night, excessive daytime work pressure leading to nervous tension, and restless minds.
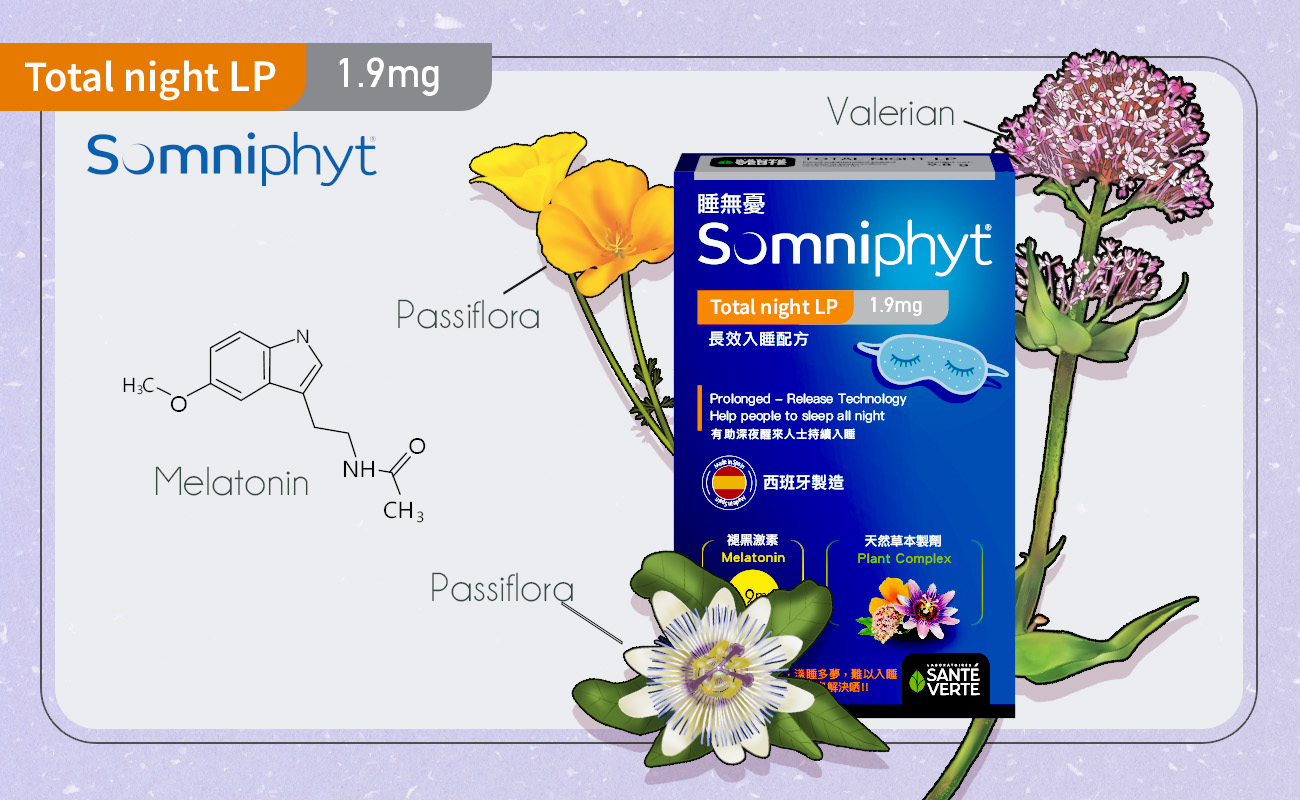
ngredients of Somniphyt® Total Night LP
Herbal Ingredients:
Passionflower:
Calms muscle tension and extreme anxiety, promotes relaxation, induces deep sleep, and increases GABA concentration, inhibiting excitability and calming the mind.
Valerian:
Induces sleep by interacting with central GABA receptors, increasing GABA levels, and reducing central nervous system activity. It also stimulates GABA release and reuptake, directly binding to GABA-A receptors.
Eschscholzia californica: Acts on GABA receptors widely expressed in the brain, mainly inhibiting interneurons in the central nervous system. It relieves stress and anxiety and induces faster sleep.
Others:
Melatonin:
Melatonin is a hormone secreted by the pineal gland in the brain, playing a vital role in regulating the body’s circadian rhythm. Melatonin levels in the human body fluctuate periodically, peaking at night and decreasing during the day. The results of a comprehensive 2013 study also show that melatonin improves primary sleep disorders, such as:
Shortening the time it takes to fall asleep
Increasing overall sleep duration and improving sleep quality. Many believe that melatonin has fewer side effects and is not addictive. Current research indicates that taking 2 mg of sustained-release melatonin daily for six months has not resulted in severe side effects, nor has long-term continuous use led to tolerance (meaning that the effects gradually decrease after continuous supplementation). If you decide to take melatonin, taking it 30 minutes before bedtime is generally recommended, starting with a low dose of 0.5 mg. If the effect is not ideal, consider increasing the dose to 3-5 mg.



