01 / 03
Azelastin-COMOD®
by Ursapharm
IntroductionMedication Usage
Azelastin-Comod®
Acute Allergies and Itching Eye
“Azelastin-Comod” is generally used to treat the following two types of allergic conjunctivitis:

Easonal allergic conjunctivitis:
This is mainly caused by the abundant pollen and spores in the air during spring and summer when flowers, plants, and trees are in bloom. The symptoms are usually short-lived and mild. Some patients with allergic rhinitis may experience symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, and wheezing.

Perennial allergic conjunctivitis:
This is usually caused by allergens that are present year-round in the environment, such as dust mites, pet dander (dog or cat hair), molds, and dust. The symptoms are similar to seasonal allergic conjunctivitis, occurring only in the conjunctiva and rarely affecting the cornea. Other allergic symptoms such as sneezing and runny nose often accompany it.
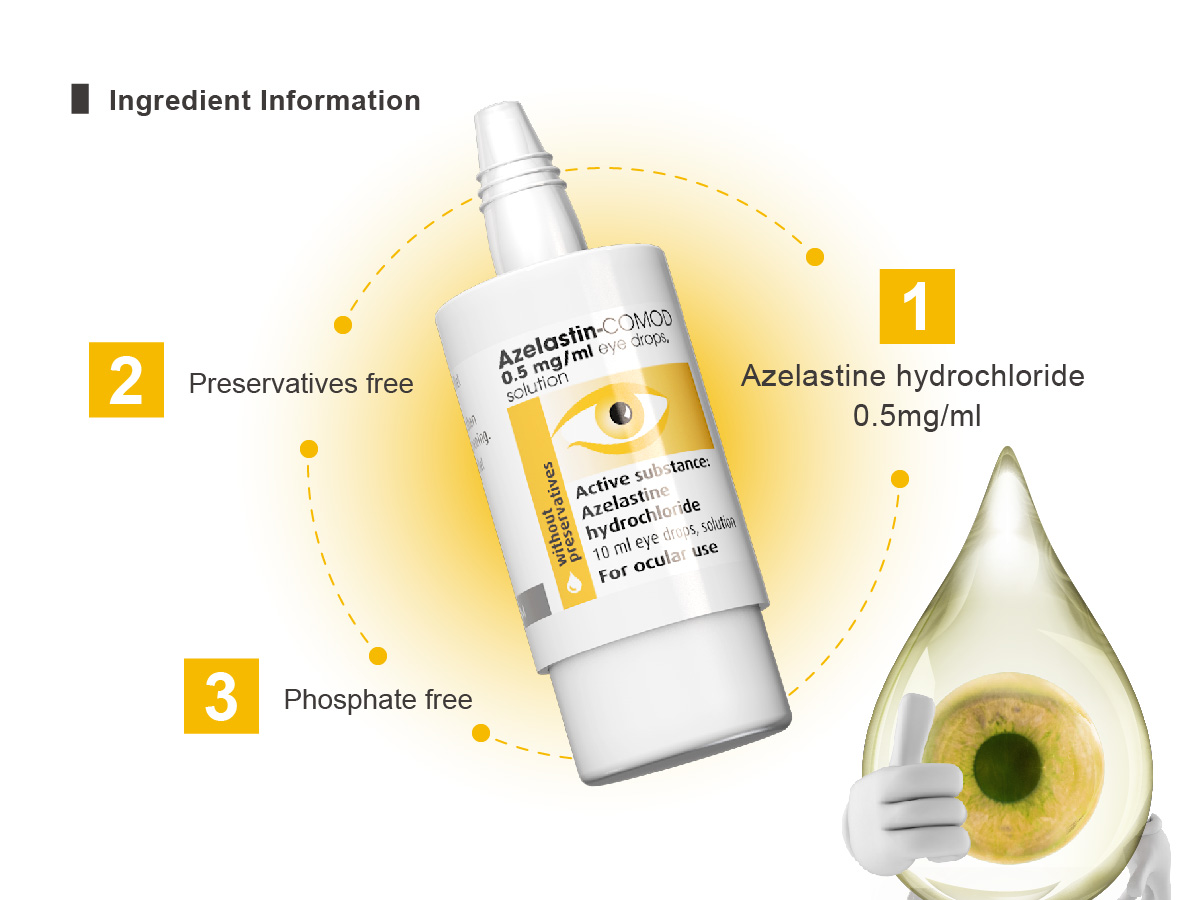
Ingredient Information
- Azelastine hydrochloride 0.5mg/ml
- Preservatives free
- Phosphate free
What is Azelastine hydrochloride?
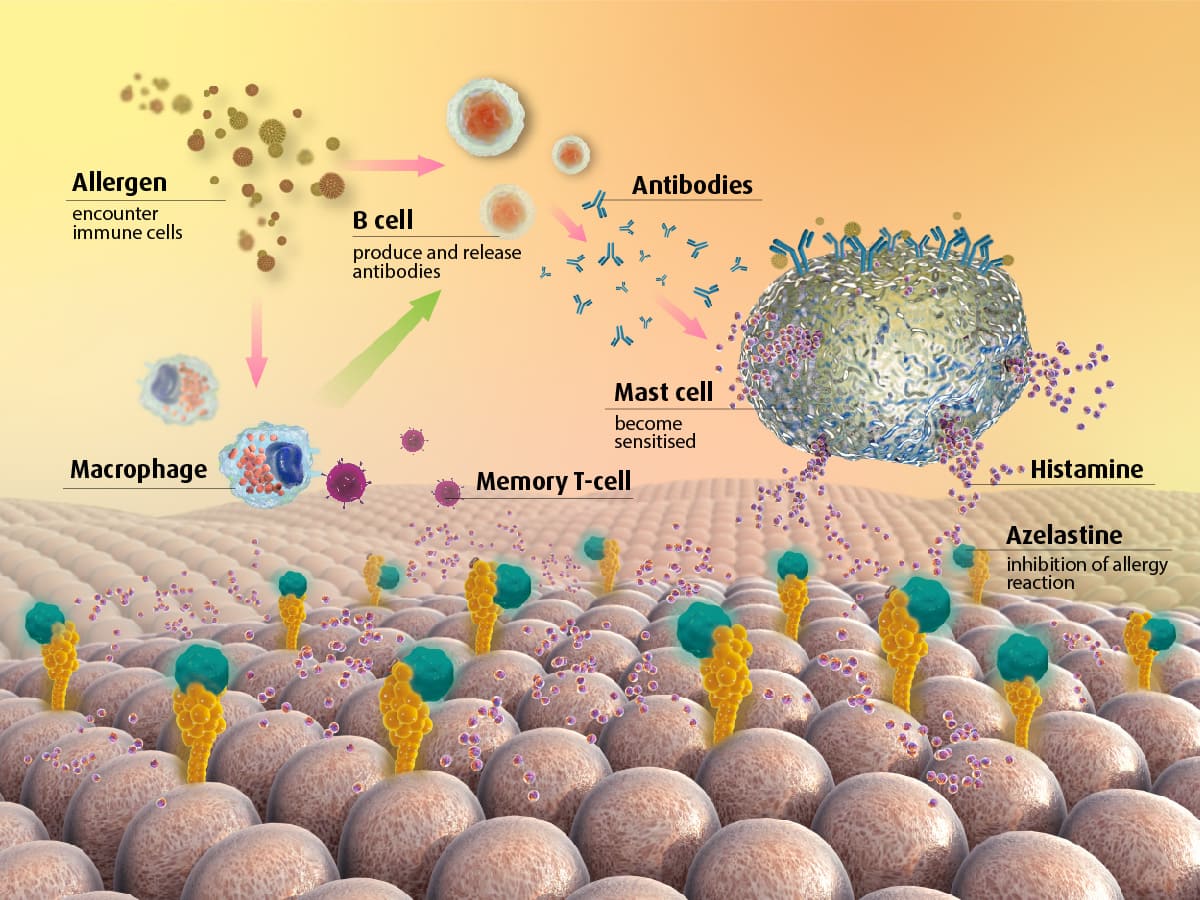
Azelastine is a second-generation H1 antihistamine ingredient. It does not pass through the blood-brain barrier, which means it does not have central nervous system side effects such as sedation or drowsiness. It is considered safe and has a longer duration of action compared to first-generation antihistamines.
Azelastine is classified as a long-acting anti-allergic compound and has strong selective blocking effects on H1 receptors. It can inhibit the synthesis and release of allergic reaction mediators, such as histamine.
Causes and Symptoms of Eye Allergies
Seasonal allergy symptoms are mostly related to pollen. Still, many other factors can also stimulate the conjunctiva of our eyes, such as animal fur, dust mites, fungal spores, insect toxins, or certain food ingredients. Patients should identify their actual allergens.
Eye allergy reactions can be very severe; the conjunctiva and mucous membranes immediately react to foreign substances, causing vasodilation and fluid release, which are common symptoms of allergies, forming “allergic conjunctivitis.”
Comod system is the new future for your eyes

The Patented System
Azelastin-COMOD® supplied in bottles with the patented COMOD® system.

Preservatives Free
The negative pressure created pulls and the flexible inner sachet more. The inner sachet stays sealed and the liquid is protected against contamination from the air.

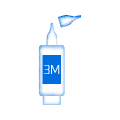
Can be used 3 months after opening
The contents remain sterile for a period of use of 3 months.

Drop-by-drop dosage
The COMOD® dosage system makes it possible to dispense exactly one drop per pump stroke.

Suitable for adults and children
Use in adults and children aged 4 years and above.Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you have other health conditions.
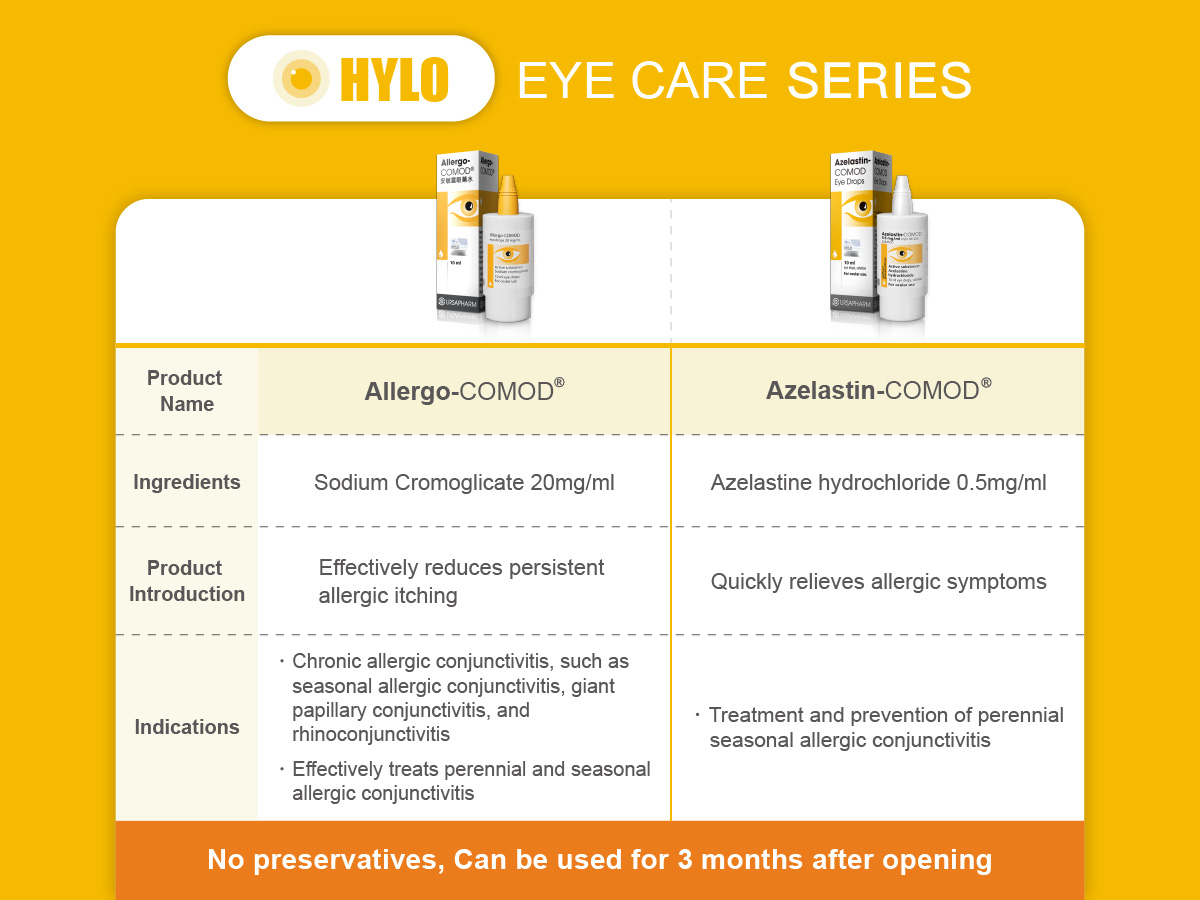
HYLO® EYE CARE SERIES
Friendly Reminder: Before using this product, please consult a specialist or professional healthcare provider if you are an infant, child, or pregnant woman.