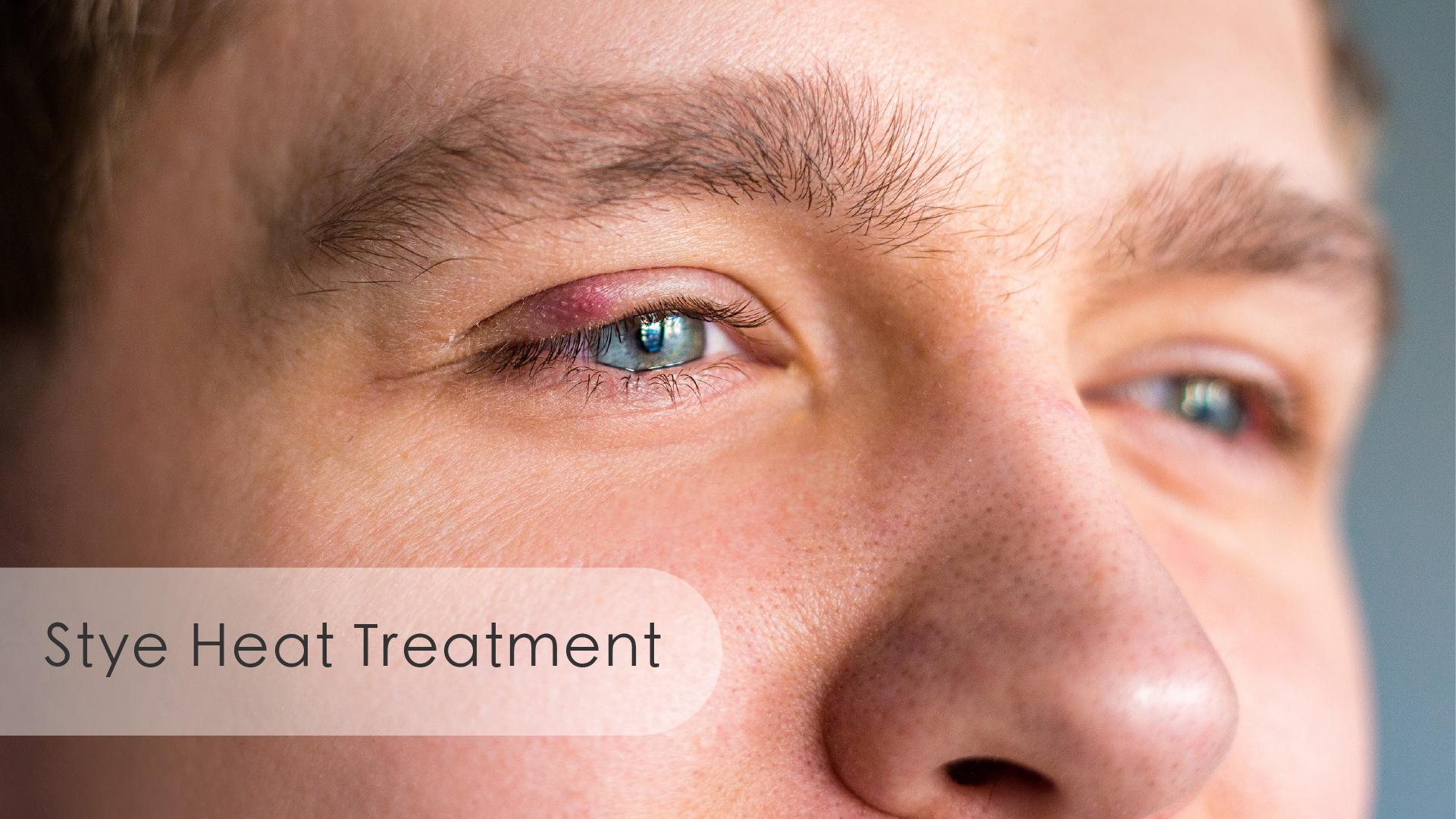
What Is a Stye?
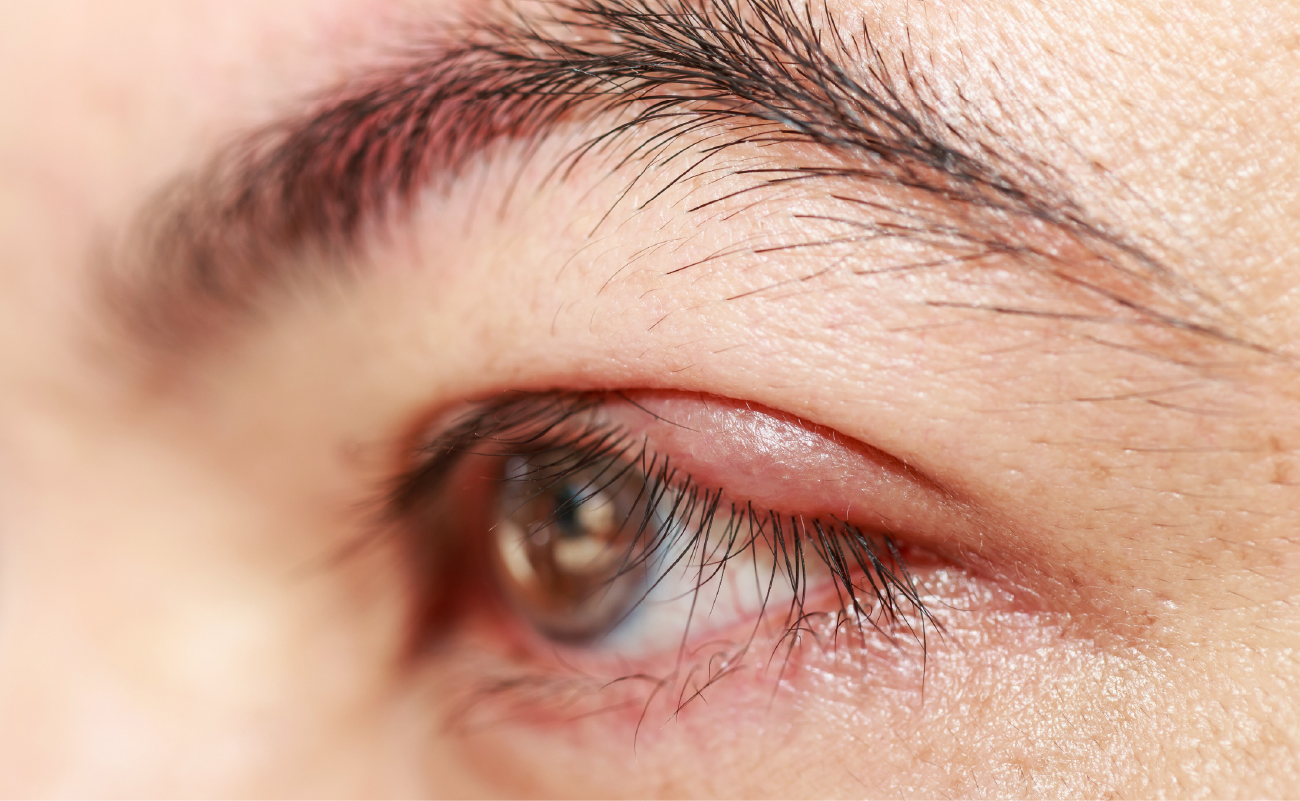
A stye, also known as a hordeolum, is a common eye condition caused by the blockage of the oil glands (Meibomian glands) along the eyelid margins. This blockage prevents the oil from draining, leading to the formation of a lump. Styes are often found at the edges of the upper or lower eyelids and sometimes on the inner side of the eyelid.
When a stye becomes infected with bacteria, it may develop into a red, swollen, and painful abscess. In severe cases, it can lead to complications such as conjunctivitis or orbital cellulitis. A stye can burst if untreated or improperly managed, potentially causing permanent eyelid drooping or vision impairment.
Common Causes of Styes
-
Infections:
Bacterial infections or infestations by Demodex mites.
-
Touching eyes with unwashed hands:
Bacteria on the hands can infect the eyelid oil glands.
-
Poor contact lens hygiene:
Not washing hands before handling or using improperly cleaned lenses.
-
Expired or contaminated cosmetics:
Bacteria from makeup products can lead to eyelid infections.
-
Inadequate makeup removal:
Residual makeup can block oil glands.
-
Excessive oil secretion:
Hormonal changes or conditions like puberty can increase oil production and gland blockage.
-
Medical conditions:
Skin disorders like dermatitis can heighten the risk of developing styes.
-
Other factors:
Weakened immunity, fatigue, or lack of sleep may contribute to stye formation.
Symptoms and Characteristics of Styes
- Redness, swelling, and pain in the eyelid.
-
- A red lump at the eyelid edge or beneath the eyelashes, sometimes developing into an abscess.
-
- Itchy eyes.
-
- Excessive tearing.
-
- A sensation of a foreign object or scratchiness in the eye.
-
- Larger styes may press against the eye, causing blurred vision.
-
- Some individuals may experience light sensitivity or temporary astigmatism.
How Long Does a Stye Take to Heal?
Styes typically heal within a few days to two weeks, depending on severity and whether an infection is present. Minor styes often resolve independently, but more severe or infected cases require medical intervention.
1. Heating pad
A heating pad helps open blocked oil glands, drain excess oil, and improve blood circulation around the eye for faster healing.
How to apply a heating pad:
- Use an eye-safe heating pad with a consistent temperature of around 45°C.
- Apply it to the eyelid 2–3 times daily for 5–7 minutes each time.
For more details, please refer to the introduction page of Posiforlid Eyelid Heating pad.
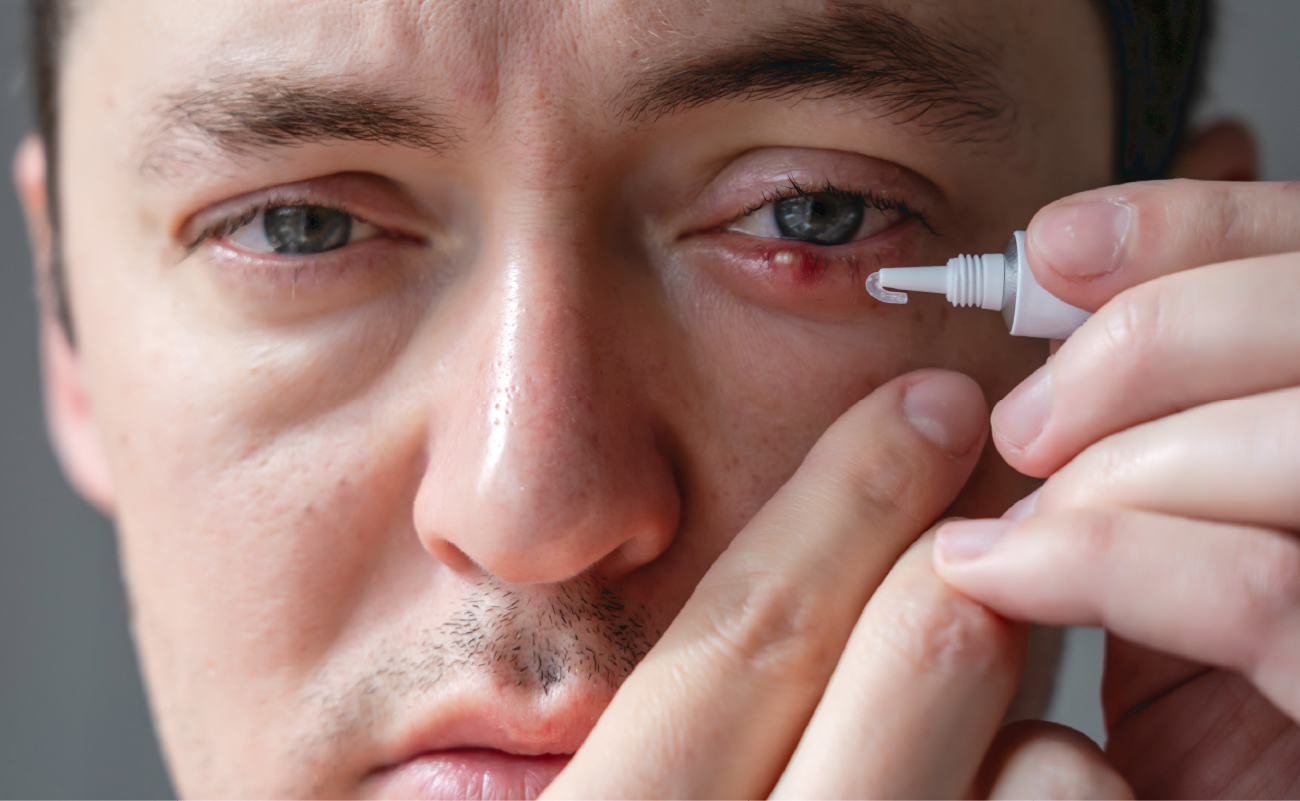
2. Anti-inflammatory Medications
Doctors may prescribe anti-inflammatory medications if the stye is infected, including antibiotic eye drops or ointments. Always follow the prescribed instructions or product guidelines.
3. Surgical Treatment
Minor surgery may be required for styes that do not resolve over time, are excessively large, or contain pus. A doctor can perform an incision to drain the abscess. This procedure typically takes 10–15 minutes, and recovery generally occurs within a few days to two weeks.
How to Prevent Styes: 3 Effective Methods
Understanding the causes of styes can help you take proactive steps to prevent them. Below are three practical prevention methods:
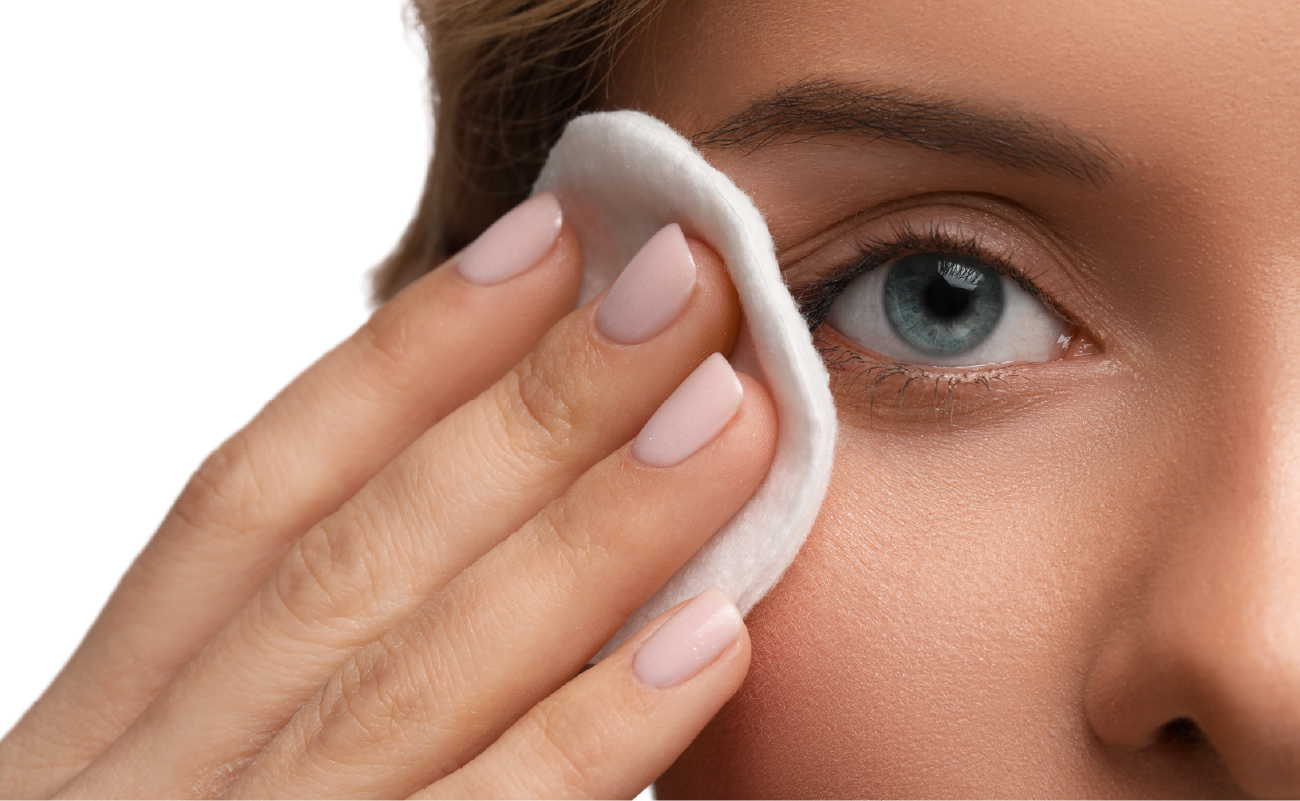

1. Hygiene and Makeup Practices
- Keep your hands clean: Always wash your hands before touching your eyes.
- Avoid rubbing your eyes: This reduces irritation and infection risks.
- Clean your eyelids regularly: Use a cotton pad with warm water for daily cleaning.
- Properly handle contact lenses: Follow the cleaning and disinfecting instructions.
- Thoroughly remove makeup: Cleanse your face and eyes thoroughly after applying makeup to prevent oil gland blockage.
- Regularly clean and replace makeup tools: Dirty and expired products can harbor bacteria.
- Avoid sharing makeup: Sharing products can spread bacteria and increase infection risks.
2. Lifestyle Habits
- Get enough sleep: Insufficient sleep weakens immunity, increasing infection risk.
- Avoid late nights: Staying up late strains the eyes, raising the likelihood of styes.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can disrupt hormone balance and oil production, heightening stye risks. Relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or exercise can help.
3. Dietary Choices
- Maintain a balanced diet: Include fruits and vegetables rich in vitamins and minerals to boost immunity.
- Reduce oily and spicy foods: These may stimulate excessive oil production, contributing to gland blockages.
- Limit consumption of irritant foods: Overeating such foods can cause eye redness. Moderate intake to promote eye health.
Daily Eyelid Care: Recommended Products
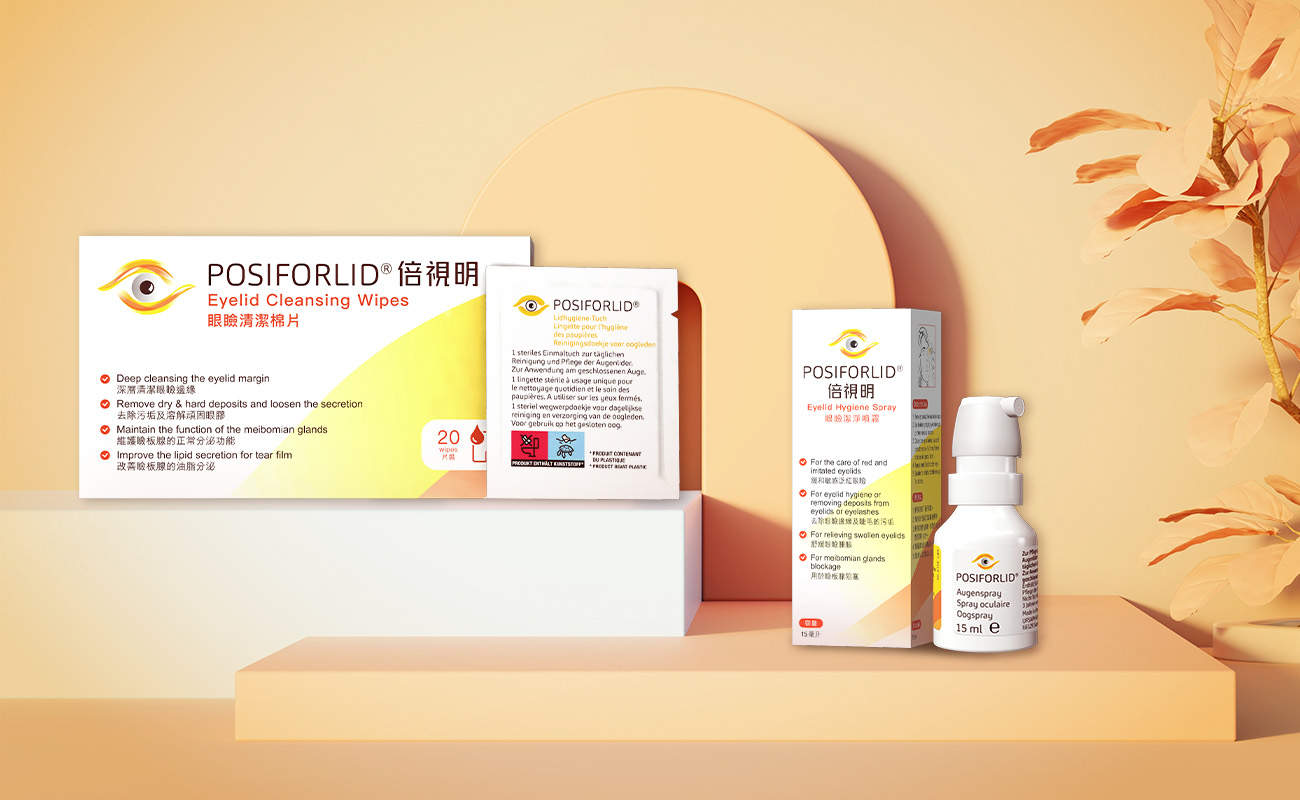
Maintaining eyelid hygiene is essential for effective prevention of styes and other eyelid conditions. We recommend daily use of Posiforlid Eyelid Cleansing Wipes and Posiforlid Eyelid Cleansing Spray.
- Posiforlid Eyelid Cleansing Wipes: These wipes are enriched with hyaluronic acid, horsetail, and euphrasia extract. They are free of preservatives and fragrances, making them ideal for sensitive eyelids. The convenient individual packaging allows you to carry them anywhere—whether at home, outdoors, or while traveling—to keep your eyelids clean and healthy.
- Posiforlid Eyelid Cleansing Spray: Designed for irritated and sensitive eyelids, this gentle formula combines euphrasis extract, hyaluronic acid, and salicylic acid. It effectively removes debris while soothing and nourishing the delicate skin around the eyes, supporting overall eye health.